The kingdom of heaven the Bible teaches about is a place without pain. How good will it be to live without feeling pain all our lives?
It would be a great thing if we were in heaven where there is no pain at all, but on the earth it is not quite a good thing for a person not to feel pain although he or she is sick.
In 2011, a movie with a unique title Pained was released. This film depicts the ironic encounter of a woman, to whom even a little pain is deadly because of her rare disease, with a man who cannot even feel the pain by losing the senses on his body from his guilt after losing his family because of his mistake. Like the story of the man who does not feel pain and the woman who cannot overlook even a little pain, it is a problem if we are too numb or too sensitive to pain. What does pain mean to our body?

Nociception is the most accurate skin sensation
Pain is an unpleasant sensation associated with, or resulting from, actual or potential tissue damage. In other words, it is an unpleasant feeling made by something that goes wrong with a part of the body; a signal is made when the pain spots scattered over the body are stimulated and it reaches the brain through the nerves, allowing the person to be aware of the pain.
More specifically, in the membrane of a cell that constitutes the pain spot, there is a pathway to transfer nociceptive substances such as serotonin and histamine into the cell. When the tissue is damaged, a nociceptive substance is formed and enters the cell through the pathway, and the cell recognizes the pain signals. The spicy taste of pepper is not a taste, but a kind of nociception caused by a substance called capsaicin. Mechanical stimuli to bump into something or be pricked with a needle, or thermal stimulus to be burned in the fire, are all the causes of pain. The perceived pain signal is transmitted along the nociceptor to its final destination—the brain.
The speed at which nociception is transmitted to the brain is 0.5 to 30 meters [approx. 1.6 to 98 feet] per second, which is slower than tactile sensation which moves at 70 meters [approx. 229 feet] per second. It is because nociceptors are so thin that they transmit signals more slowly than other sensory nerves. While there are about 25 tactile spots per square centimeter of skin on average, the number of pain spots is close to 200 per square centimeter of skin. This is possible because nociceptive nerves are thin. As there are many pain spots, we can know painful spots more accurately.

Danger signal from the body
The life of patients suffering from feeling severe pain even for little irritation was introduced on TV and made people feel bad. Even the smallest irritation makes patients painful, who suffer from a rare disorder called Complex Regional Pain Syndrome [CRPS]. They feel extreme pain as if they were being pricked with a needle or struck with an ax when someone just brushes past them. Even after the stimulus has disappeared, the pain doesn’t easily subside. Sometimes, patients who are always suffering from pain feel depressed or suicidal. A life of a person whose senses only feel pain is cruel. If that’s the case, would it be better not to feel pain at all?
Cell’s Pain Signal Recognition Process
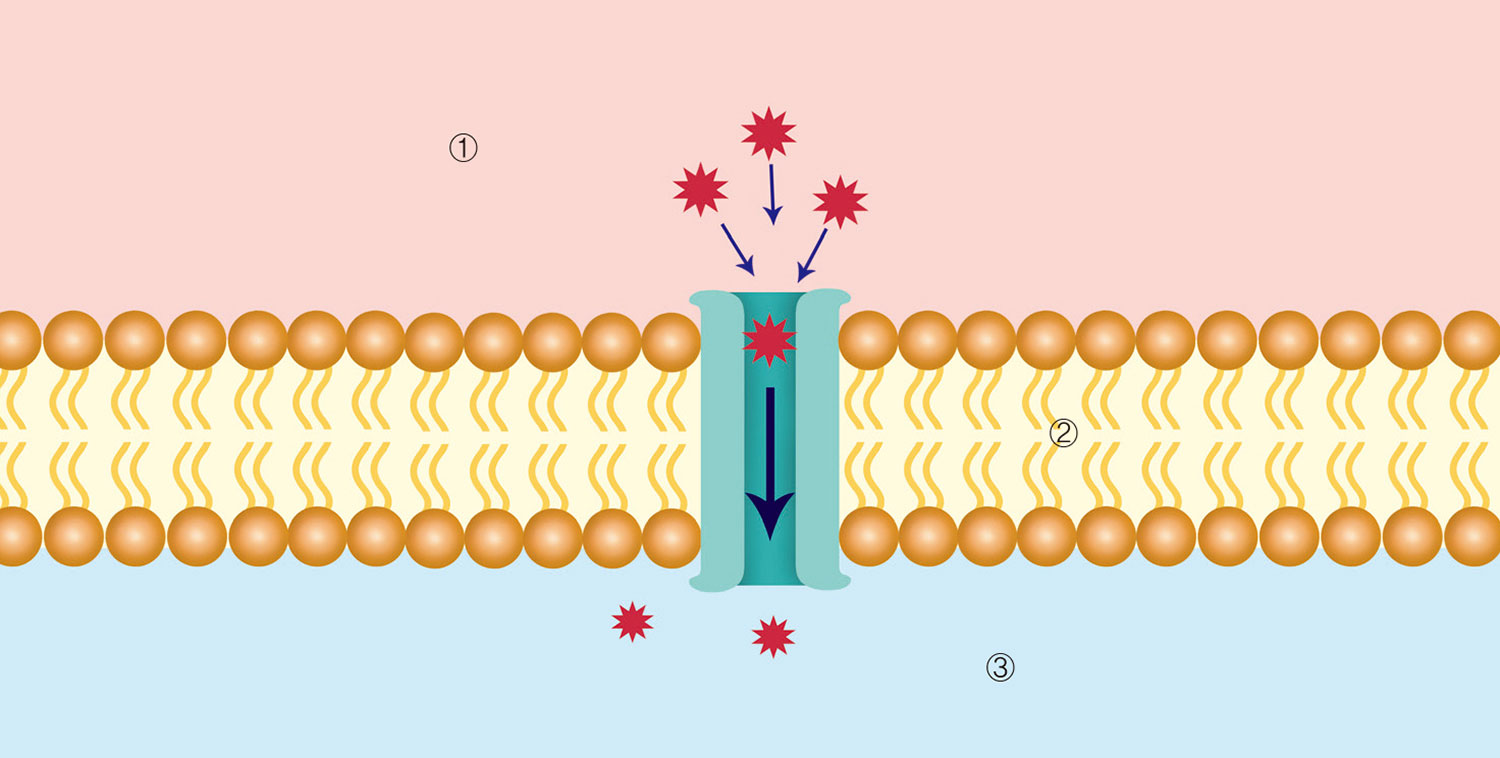
② Cell membrane: The produced nociceptive substance enters the cell through the passage of the cell membrane.
③ Inside the cell: The cell recognizes the pain signal.
A girl named Gabby Gingras was on a famous talk show in the U.S. in 2005, and became the talk of the country, being called superwoman. She felt no pain even when she touched a hot iron with her hand, or stepped on broken pieces of glass. The girl suffering from analgesia didn’t feel pain even when she was stung or hit by something. She couldn’t sense pain because there was something wrong with her neurotransmitter circuits or her brain itself. The causes of analgesia are very diverse; it can be from anthropogenic factors like drugs, or accidental injuries, or chronic diseases such as diabetes.
Patients with analgesia, who are insensitive to physical impairment, are often at risk because they cannot take appropriate measures to protect their bodies. Gabby’s cornea got wounded as she habitually rubbed her eyes. However, as she didn’t feel pain, she failed to receive treatment for it at the right time and her eye went blind. Joanne Cruz, another patient with analgesia, did not scream even once when she delivered her baby. She had to undergo surgery to put a metal pin on her spine because she left her back untreated even though she had twisted it, and later she had to undergo bigger surgery because she didn’t realize that her metal pin she got in the previous surgery had broken. Some patients with analgesia cannot live alone because they don’t feel hungry, and quite many people die as their appendicitis that can be treated with simple treatment becomes worse because they cannot feel stomachache.
Insensitivity to physical impairment is not only the case of patients with analgesia. While there are a large number of pain spots in the skin, the number of pain spots in internal organs is only one-fiftieth, compared with the skin. This is the reason lung cancer is not found until the late stage in most cases, and neither is liver which is called a “silent organ.” Patients complain of pain only when their condition becomes severe.
It is not a fortune but a disaster to be unable to feel pain; if you cannot feel pain, you will not know where your problem is in your body, which makes you endanger your life even with small wounds. The reason nociception is the most developed sense among the senses is that the body needs to be protected from external dangers by quickly identifying the problems with our body and taking action accordingly.
To overcome pain
The sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached even after losing it in an accident or through surgery is called “phantom limb.” Patients who feel phantom limb experience the pain from their missing limbs, which is called “phantom limb pain.” It occurs as the nerve cells of cerebrum responsible for senses cause illusion, and this makes patients more painful because they can neither scratch nor massage the itchy and painful limbs that are not even there.
As pain is felt by the brain, sometimes the phantom limb pain is treated by using the flexibility of the brain. It is to make the patients feel like they have limbs on both sides by reflecting their existing limb in the mirror. Patients who have lost their arms and have been suffering from the phantom limb pain feel like their missing arms are moving while looking at their existing arms moving in the mirror. Then the pain is reduced. It is to reduce the pain by making the brain, which misunderstood that their missing arms felt painful, understand that there is no pain through a visual effect.
Morphine which is extracted from drugs is addictive, but it is used as an analgesic to relieve pain very effectively. Morphine produces analgesic effect by combining with special proteins in the brain. Just as only the right key can open the lock, special proteins combine only with certain types of material. This means that there is a substance acting like morphine in our body.

In 1975, a substance that has an analgesic effect 100 times stronger than that of morphine was found in the brain. It is enkephalin which is a kind of endorphin. When the brain recognizes pain, it secretes endorphins which suppress pain and interfere with pain transmission. In other words, the body controls the pain to overcome it. When marathoners are out of breath near the finish line and their hearts feel like exploding, they experience a “runner’s high” which is an exciting feeling of joy, instead of pain; and mothers sometimes feel strong joy during delivery. It is because endorphins are released to endure severe stress or physical pain. Endorphins are known to be secreted a lot when laughing, but in fact they are released the most when physical and mental pain reaches its peak. The types of endorphins that have been discovered so far include enkephalin, beta endorphin, and dynorphin.
Pain is an indispensable part of our lives. Sometimes, pain comes to us as unbearable suffering, but behind it there is a warning telling us the dangers of your body. Beyond suffering, pain is evidence that we are alive and a system of warning that protects us.